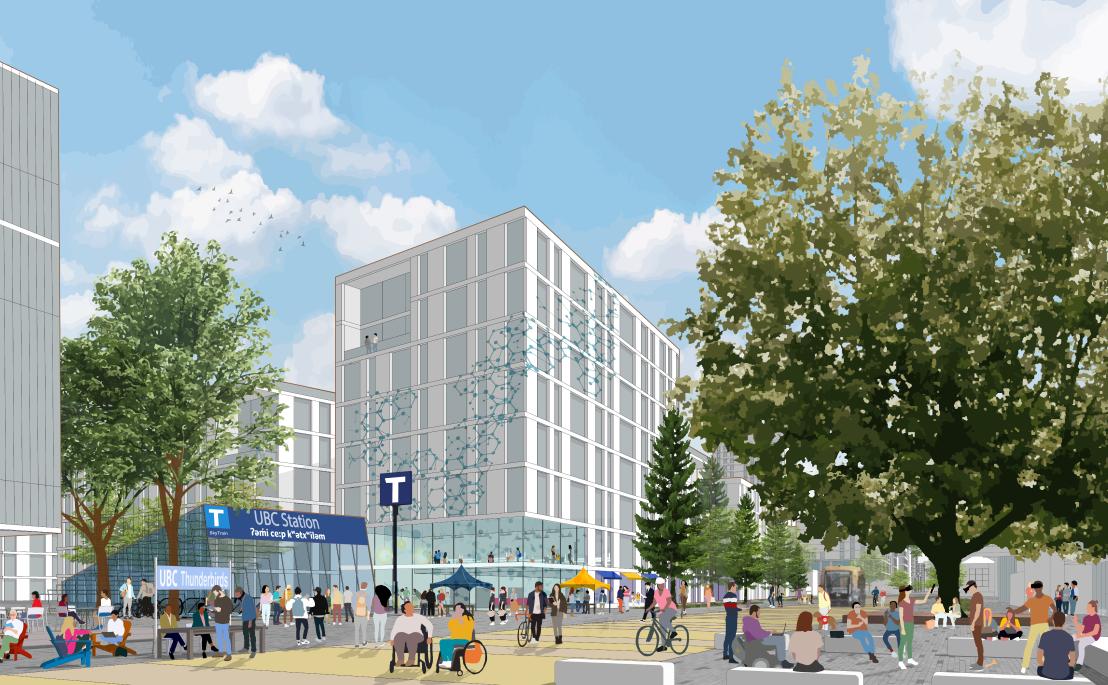

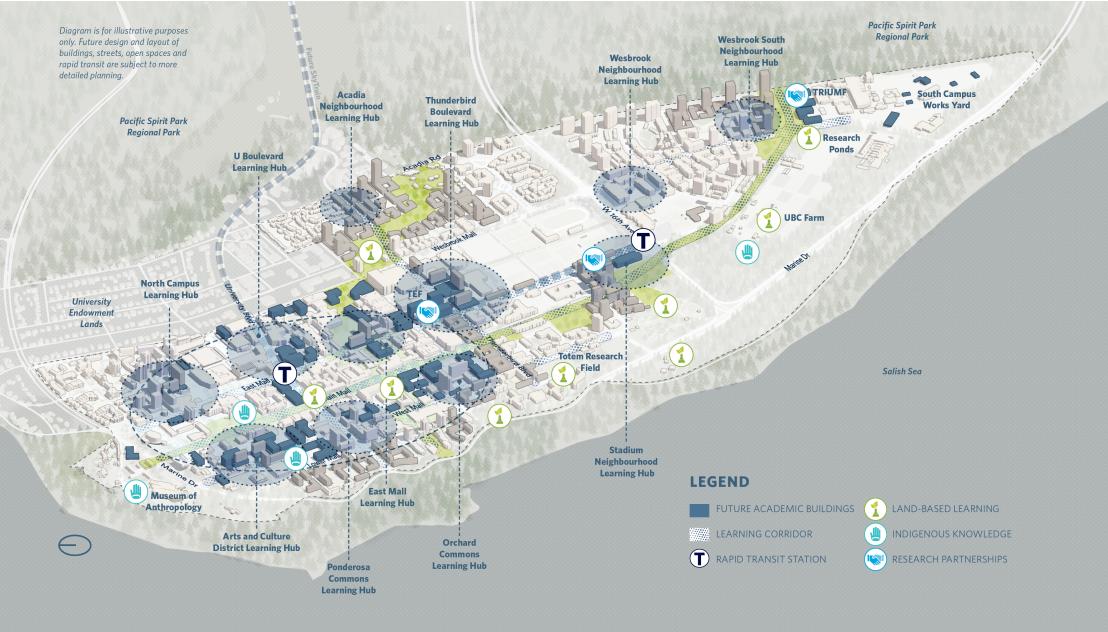
UBC Vancouver in 2050
With a daytime population of over 100,000 people, the campus is a place of learning, showcasing UBC teaching, research and innovation. Collaboration, creativity and knowledge exchange, and Musqueam and Indigenous knowledge are prioritized through inviting, accessible and flexible buildings and outdoor spaces for all. More than ever before, the campus is a test bed, incubator and role model for novel approaches to planning and implementing low carbon communities, translating new knowledge into practice, and attracting industry, Musqueam and community partnerships. Blurring the divide between academic and neighbourhood activities in formal and informal spaces throughout the campus and neighbourhoods encourages impromptu encounters that foster learning, discovery and community and unlock synergies between UBC’s communities.
Key Strategies
|
Concentrating Academic Growth in the Campus Core
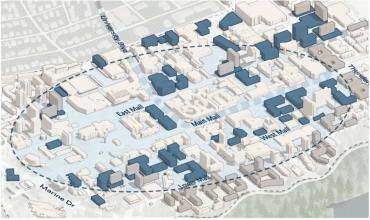
The Vision maintains the approach of building and renovating academic spaces within the campus core, emphasizing new growth in proximity to the future rapid transit station on University Boulevard and along East Mall and West Mall.
More Learning Hubs
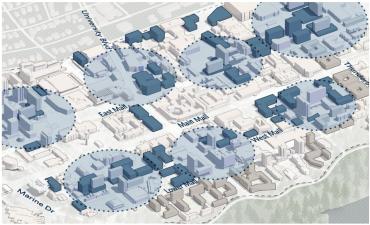
The Vision identifies sites for new Learning Hubs, which are developments that mix student and neighbourhood housing, academic/knowledge sharing space and amenities.
Learning Corridors
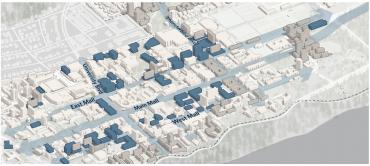
The Vision enables stronger, more defined connections between Learning Hubs and other centres of activity. A series of Learning Corridors will intensify academic capacity along East Mall, West Mall and Thunderbird Boulevard to support transit-oriented development, increase vibrancy and connect to research partnership sites and housing opportunities.
Learning Everywhere

While academic growth will continue to be concentrated in the campus core, along corridors and in Learning Hubs, the entire campus, including the neighbourhoods, continue to offer significant opportunities to support teaching, learning and research.
Here are some current examples of learning happening outside the classroom:

